Categories
Understanding Blood Disorders in Children: Symptoms & Treatments
Jul 18, 2025
When it comes to a child’s health parents are often on high alert for fevers, infections, or injuries. However, in few children less visible blood disorders can significantly affect growth, immunity, and well-being. These conditions can be inherited or acquired and may appear as tiredness, frequent infections, pale skin, or unexplained bruises. Understanding the early signs and knowing when to see a child specialist can make a meaningful difference in your child’s life.
At Rainbow Children’s Hospital, our dedicated team of pediatric hematologists and child specialists works closely with families to diagnose and treat a wide range of blood-related conditions in children, offering compassionate, evidence-based care.
Some blood disorders are mild and temporary, while others are chronic and require ongoing medical care. Early detection and timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Our pediatric diagnostic facilities at Rainbow Hospitals have the latest technology to ensure accurate and timely results, helping families confidently move forward.
We also encourage regular follow-ups, vaccinations, nutritional guidance, and emotional support to help children live active, fulfilling lives.
Rainbow Hospitals is among Hyderabad's most trusted children’s hospitals, known for its expert team, child-friendly environment, and advanced facilities. Our child specialists are trained to look beyond the obvious, ensuring that no detail is missed in pursuing your child’s health and happiness.
Blood disorders in children can be severe, but with the correct diagnosis, care, and support, many of these conditions can be effectively managed or even cured. Your awareness and timely action can make a huge difference as a parent.
At Rainbow Hospitals, our focus is not just on treating the illness but on nurturing the child and supporting the family through every stage of care.
If you have any concerns about your child’s health, contact our experienced child specialists. We are here to help you every step of the way.
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this blog is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition, symptoms, or treatment options. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read here.
At Rainbow Children’s Hospital, our dedicated team of pediatric hematologists and child specialists works closely with families to diagnose and treat a wide range of blood-related conditions in children, offering compassionate, evidence-based care.
What Are Blood Disorders in Children?
In children, blood disorders affect one or more components of the blood, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, plasma, or the bone marrow where blood is produced. These disorders may impact how oxygen is carried through the body, how well a child fights infection, or how the blood clots.Some blood disorders are mild and temporary, while others are chronic and require ongoing medical care. Early detection and timely intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Common Types of Blood Disorders in Children
Anemia
Anemia is one of the most common blood disorders in children. It occurs when insufficient healthy red blood cells carry oxygen to the body’s tissues. Iron-deficiency anemia is often seen, but other forms include thalassemia and sickle cell anemia.Thalassemia
Thalassemia is a genetic condition where the body produces abnormal hemoglobin. Thalassemia may cause fatigue, bone deformities, and delayed growth depending on the severity. Regular blood transfusions and iron chelation therapy are often needed.Sickle Cell Disease
An inherited disorder, sickle cell anemia causes red blood cells to become crescent-shaped and less flexible, which can block blood flow and cause pain, infections, or even organ damage. Treatment focuses on preventing complications and managing symptoms.Hemophilia
A rare but serious disorder, hemophilia affects the blood’s ability to clot. Children with this condition may bleed longer after injuries or may have spontaneous bleeding episodes. Clotting factor replacement therapy helps control the condition.Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP)
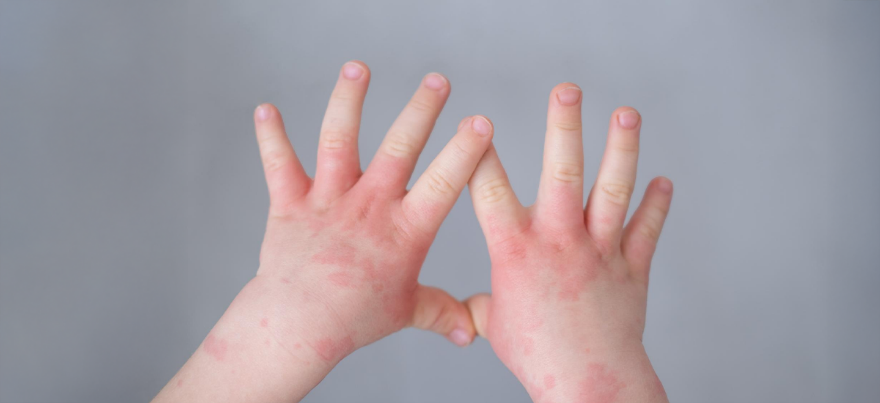
In ITP, the body’s immune system attacks its platelets, leading to easy bruising, nosebleeds, or small red dots on the skin. Most cases resolve independently, but some may require medication or monitoring.Leukemia
Leukemia is type of cancer starts in the bone marrow and leads to the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells. Though frightening, leukemia in children has a high rate of treatment success when diagnosed early and managed by an experienced team.Common Symptoms to Watch Out For
Blood disorders can sometimes be subtle in their early stages. Here are some signs that should prompt a visit to a child specialist:- Persistent fatigue or weakness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Frequent or severe infections
- Easy bruising or prolonged bleeding
- Bone or joint pain
- Swollen lymph nodes or abdomen
- Unexplained weight loss
- Tiny red spots on the skin (petechiae)
How Are Blood Disorders Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination by a child specialist. Blood tests, such as a Complete Blood Count (CBC), peripheral smear, and iron studies, are common first steps. Advanced tests like genetic screening, bone marrow biopsy, or coagulation studies may be recommended depending on the suspected disorder.Our pediatric diagnostic facilities at Rainbow Hospitals have the latest technology to ensure accurate and timely results, helping families confidently move forward.
Treatment Options
The treatment plan depends on the specific condition, its severity, and the child’s overall health. Options may include:- Iron or vitamin supplements for nutritional anemia
- Medications or steroids for autoimmune conditions like ITP
- Blood transfusions in cases of thalassemia or sickle cell disease
- Clotting factor infusions for hemophilia
- Chemotherapy and targeted therapy for leukemia
- Bone marrow transplant for certain cancers or severe genetic conditions
Living with a Blood Disorder
Managing a chronic blood disorder can be challenging for both the child and the family. From medication schedules to hospital visits, it can feel overwhelming. At Rainbow Hospitals, our multidisciplinary team, including pediatricians, child specialists, hematologists, nutritionists, and counsellors, walks with you every step.We also encourage regular follow-ups, vaccinations, nutritional guidance, and emotional support to help children live active, fulfilling lives.
When to Consult a Child Specialist?
If your child shows any symptoms mentioned above, or if there is a family history of blood disorders, it is best to consult a qualified child specialist without delay. Early evaluation can lead to better treatment options and fewer complications.Rainbow Hospitals is among Hyderabad's most trusted children’s hospitals, known for its expert team, child-friendly environment, and advanced facilities. Our child specialists are trained to look beyond the obvious, ensuring that no detail is missed in pursuing your child’s health and happiness.
Blood disorders in children can be severe, but with the correct diagnosis, care, and support, many of these conditions can be effectively managed or even cured. Your awareness and timely action can make a huge difference as a parent.
At Rainbow Hospitals, our focus is not just on treating the illness but on nurturing the child and supporting the family through every stage of care.
If you have any concerns about your child’s health, contact our experienced child specialists. We are here to help you every step of the way.
FAQs
1. What are the warning signs of blood disorders in children?
Early symptoms include fatigue, pale skin, frequent infections, easy bruising, unexplained bleeding, or red spots on the skin. If these persist, it’s important to consult a pediatrician or child specialist for blood tests and evaluation.2. Are all blood disorders in children genetic?
Not always. Some, like thalassemia and sickle cell anemia, are inherited, while others, such as iron-deficiency anemia or ITP, may be caused by nutritional gaps, infections, or immune responses. Early diagnosis helps determine the root cause.3. Can blood disorders in children be cured?
Yes, many blood disorders can be treated effectively or even cured, especially if detected early. Treatments may include medications, blood transfusions, supplements, or in severe cases, bone marrow transplants. Outcomes are often positive with timely care.Disclaimer:
The information provided in this blog is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition, symptoms, or treatment options. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read here.